Introduction
Data is the lifeblood of every organization, and safeguarding it against potential threats is a critical responsibility. As businesses undergo digital transformation and implement Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solutions like Oracle NetSuite, data security and compliance become paramount. Oracle NetSuite, as a cloud-based ERP system, stores and processes vast amounts of sensitive business data, including financial records, customer information, and intellectual property. Ensuring the security and compliance of this data throughout the implementation process is vital to protecting an organization’s reputation, financial stability, and legal standing. In this article, we will explore the importance of data security and compliance during Oracle NetSuite implementation and discuss essential measures to safeguard data effectively.
Understanding Data Security in Oracle NetSuite Implementation
Data security is the practice of protecting data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. In an Oracle NetSuite implementation, data security encompasses various layers of protection, including network security, access control, encryption, and monitoring. It involves a combination of technical, procedural, and administrative measures to safeguard data throughout its lifecycle.
The Role of Oracle NetSuite's Security Features
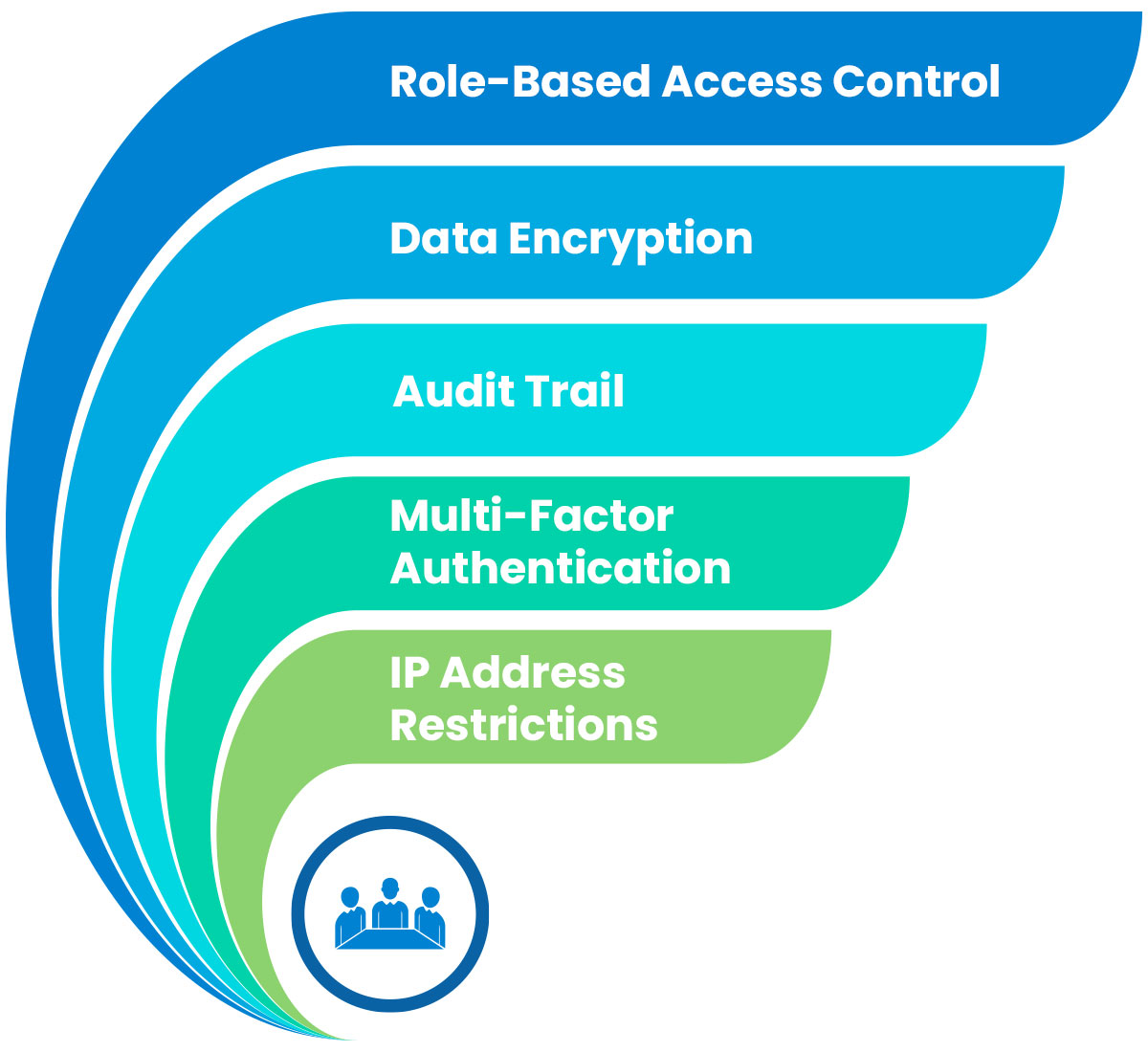
- Role-Based Access Control: Oracle NetSuite allows administrators to define roles and assign specific permissions to users based on their job functions. Role-based access control ensures that users can access only the data and functionalities necessary for their roles, limiting the risk of unauthorized access.
- Data Encryption: Oracle NetSuite encrypts data both in transit and at rest using industry-standard encryption algorithms. This ensures that sensitive information remains unreadable and secure, even if intercepted by unauthorized individuals.
- Audit Trail: Oracle NetSuite maintains a detailed audit trail, recording all activities related to data access, modification, and deletion. The audit trail serves as a crucial tool for detecting and investigating any suspicious or unauthorized activities.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Oracle NetSuite supports MFA, adding an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification before accessing the system.
- IP Address Restrictions: Administrators can define IP address restrictions to control access to Oracle NetSuite from specific geographic locations or trusted networks, further enhancing security.
Complying with Industry Regulations
Data security is closely linked to regulatory compliance. Organizations in various industries are subject to data protection laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the healthcare sector, and the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) for financial reporting. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in severe penalties, reputational damage, and legal liabilities.
During Oracle NetSuite implementation, organizations must ensure that their data security measures align with the requirements of relevant industry regulations. This may involve implementing additional security controls, data access restrictions, and data retention policies to meet compliance obligations.
Securing Data Migration
Data migration is a critical aspect of Oracle NetSuite implementation, involving the transfer of data from legacy systems to the new ERP platform. During this process, sensitive data is particularly vulnerable to breaches and exposure. Ensuring data security during migration is essential to prevent data loss or unauthorized access.
To secure data migration, organizations can take the following measures:

- Conduct Data Privacy Impact Assessments (DPIAs): Assess the risks associated with data migration and identify potential security vulnerabilities. Implement mitigation strategies to address any identified risks.
- Encrypt Data in Transit: Encrypt data during transfer between the legacy system and Oracle NetSuite to prevent interception by unauthorized parties.
- Validate Data Integrity: Verify data integrity after migration to ensure that no data was lost or corrupted during the transfer process.
- Limit Access to Data Migration Tools: Restrict access to data migration tools and credentials to authorized personnel only.
Employee Training and Awareness
Human error is one of the most common causes of data breaches. Employees may inadvertently click on phishing emails, share sensitive information with unauthorized parties, or fail to follow security protocols. Therefore, comprehensive employee training and awareness programs are essential to reinforce data security best practices and educate staff about the potential risks and consequences of data breaches.
Organizations should regularly conduct security training sessions, educate employees on identifying and reporting suspicious activities, and encourage a security-conscious culture throughout the organization.
Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
To ensure the ongoing effectiveness of data security measures, organizations should conduct regular security audits and penetration testing. Security audits assess the overall security posture of the Oracle NetSuite implementation and identify areas for improvement. Penetration testing involves simulating real-world cyber-attacks to identify potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the system.
Based on the findings of security audits and penetration testing, organizations can implement necessary security updates and enhancements to fortify their data protection measures.
Data Backups and Disaster Recovery
Data backups and disaster recovery planning are essential components of data security. In the event of a cyber-attack, system failure, or natural disaster, data backups ensure that critical information can be recovered and restored to minimize downtime and data loss.
Organizations should implement a robust data backup strategy, including regular backups stored in secure locations separate from the production environment. A comprehensive disaster recovery plan outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a data breach or system outage, ensuring a swift and efficient response to mitigate potential damages.
Collaboration with Security Experts
Implementing and maintaining robust data security measures can be complex, requiring specialized expertise in cybersecurity. Organizations can benefit from collaborating with security experts or partnering with managed security service providers (MSSPs) to enhance their security capabilities.
MSSPs can offer continuous monitoring, threat detection, and incident response services, providing organizations with proactive security measures and rapid response to security incidents.
Conclusion
Ensuring data security and compliance in Oracle NetSuite implementation is a critical responsibility for organizations seeking to protect their sensitive information, maintain regulatory compliance, and safeguard their reputation. By leveraging Oracle NetSuite’s built-in security features, complying with industry regulations, securing data migration, and implementing employee training programs, organizations can create a robust data security framework.
Regular security audits, penetration testing, data backups, and collaboration with security experts further strengthen an organization’s data security posture. A proactive approach to data security and compliance during Oracle NetSuite implementation helps organizations establish a strong foundation for data protection and confidently embrace the transformative potential of their ERP platform.